Abstract
This is a psychiatrist’s journey through teaching, research and making friends of professional colleagues. It also chronicles the research done in the Department of Psychiatry at KEM Hospital, Mumbai, India and the important influences over the author’s life.
Keywords: Clinical Research, Department of Psychiatry, KEM Hospital, Psychiatric Camps, Psychiatric Treatments, WHO International Collaborative Studies
Introduction
I take this opportunity to express my gratitude to my M.D. Teachers: Dr. J.C. Marfatia, Dr. S. M. Lulla, Dr. A. P. Patkar, Dr. V.G. Joshi, Dr. S. D. Dastoor and Dr. B.H. Vaidya.
I joined my Unit in the Department of Psychiatry at the KEM Hospital in the year 1970, which had stalwarts like Dr. V.N. Bagadia and Dr. L. P. Shah. Dr. Bagadia was a brilliant clinician, an inspiring, encouraging and dynamic leader with an excellent grip on social aspects of the subject, and a leader in the Indian Psychiatric Society. My entry in the Department of psychiatry coincided with Dr. Bagadia’s installation as President of Indian Psychiatric Society at its Madurai Annual Conference held in 1971. That was also my first National Conference.
I attended the Inaugural Conference of the IPS West Zone held in Marol, Ubhrat in Gujrat in September 1970. It was organised by Dr. Ishwar Desai and Dr. Jagdish Desai of Navsari, Gujarat. There was great enthusiasm at this conference. This was my first opportunity to meet delegates from Mumbai, Maharashtra and Gujarat and the first opportunity to read a paper on an anti-anxiety Drug.
After this beginning, I attended every West Zone and National Conference, presenting one or more papers. I looked to these as opportunities for academic interaction with other psychiatrists from various cities and regions, make professional friendships, interacting cordially with them and the organizers, and also do some sightseeing with my family. Lastly I enjoyed singing Hindi film songs at the time of Banquets, and would like to believe the delegates enjoyed it too.
I forged many friendships due to these Zonal and National Meets. Today I have friends like Dr. V. D. Shah, Dr. Pratap Mehta, Dr. Anil Shah, Dr. Maniar and Dr. Chudgar from Gujarat and many others from there. Dr. Moholkar, Dr. Burte, Dr. P.S. Sathye, Dr. Luktuke, Dr. S.M. Sule, Dr. Barhale, Dr. Kelkar, Dr. Saoji and many others from Maharashtra. Dr. Sukerkar, Dr. Pai — Dhungat, Dr. Hegde and others from Goa. From the National IPS body, I got the chance to be friendly with Dr. N. N. Wig, Dr. V.K. Varma, Dr. A. K. Agarwal, Dr. Somsundraram, Dr. Nagraj, Dr. Ramchandran, Dr. Kumar, Dr. Bhide, Dr. Venkat Ramaiya, Dr. D. Mohan, Dr. Dash, Dr. Choudhari, Dr. Chatterjee, Dr. Bhattacharya, Dr. Ajita Chakraborty, Dr. Nandi, Dr. Boral, Dr. Golecha and many more from the states like Punjab, U.P., Bihar, West Bengal, Odisha etc.
I continued to meet them every year. The academic and social interactions with them have been enriching, and this is an important part or my composite experience as a psychiatrist and as a person.
Clinical Research in the Department
Psychosocial and other psychiatric studies of all psychiatric and psychosomatic disorders and their proper treatment for good enduring results were Dr. V.N. Bagadia’s goals, shared by Dr. L.P. Shah and myself. Similarly, psychosocial and other psychiatric studies of Schizophrenia (Bagadia et al., 1973,[8] Bagadia et al., 1979,[1] Depression (Bagadia et al., 1979,[16] Suicidal attempt, Epilepsy (Bagadia et al., 1973,[11] Male Sexual dysfunction (Bagadia et al., 1972,[6] Bagadia et al., 1983),[2] Alcoholism (Bagadia et al., 1979[14]) and Disulfiram (Bagadia et al., 1982),[7] Cannabis Abuse (Bagadia et al., 1976),[10] Hysteria, Anxiety disorder, Phobia, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (Pradhan et al., 1984[20] was also our priority. Data on patients seen in 1-year were entered on well-prepared proformas. Data analysed were discussed in detail to understand the overall profile of each of these disorders, to draw relevant conclusions, and for management and further understanding.
Some other important studies in Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry, Psychosomatic disorders and some other Special issues were also undertaken. Some of them were as follows. Detection of Psychiatric Disorders in medical out patients over 1-year, Psychiatric Study of Diabetes Mellitus (Bagadia et al., 1973),[12] Chronic Dermatitis (Bagadia et al., 1998),[3] Metropathia hemorrhagica, Vertigo, Hyperhydrosis (Pradhan et al., 1984),[19] Writer’s Cramp, Sydenham’s Chorea, as also quite a few smaller studies.
WHO International Collaborative Studies
WHO International Collaborative Studies were undertaken in our Unit of the Department. These studies evaluated (1) dose effective evaluation of antidepressant medication (Gada et al., 1984[18]) (2) dose effective evaluation of antipsychotic medication in Schizophrenia (Gada et al., 1973[17]) (3) comparative efficacy of Counselling versus Benzodiazepine in mild Anxiety Disorder (Bagadia et al., 1988[15]) (4) death and dying experiences (Singh et al., 1988,[23] etc.
These were intensive research studies using standardised interviews and rating scales. Active interaction took place with other Centers from London, Tokyo and Nigeria, and with additional experts from Moscow, U.S.A. and Geneva. The results of these studies have been published by the W.H.O.
We had bright and dedicated Senior Research fellows working for these studies. They were Dr. M.T. Gada, Dr. V.K. Mundra, Dr. P.D. Lakdawala, Dr. R.R. Abhyankar, Dr. K.S. Ayyar, Dr. B. R. Agarwal, Dr. Ajai R. Singh and Dr. I. R. Rajkumar, amongst others who assisted as Senior Research Fellows.
Psychiatric Treatments
Behaviour therapy
Responding to my initiative and enthusiasm, Dr. V. N. Bagadia created a Behaviour Therapy Sub-unit and placed it under my supervision. Behaviour Therapy studies of Phobic disorder, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, Anxiety Disorder, Alcoholism (Bagadia et al., 1979,[14]) Writer’s Cramps, Male Sexual Dysfunction (Bagadia et al., 1983),[2] Hyperhydrosis (Pradhan et al., 1984[19] and Homosexuality (Pradhan et al., 1982a;[21] Pradhan et al., 1982b[22]) were done in a systematic manner. The studies were presented at various Conferences and published. Behaviour Therapy subsequently became a routine in the private practice of many Consultant Psychiatrists as well as in General Hospitals in Mumbai and elsewhere.
Drug trials and use of newly introduced drugs
I was part of many drug trials on new medicines like Pimozide (Bagadia et al., 1973;[9] Bagadia et al., 1976),[4] Dothiepin, Piportil Hydrochloride C Depot Antipsychotic (Bagadia et al., 1979),[5] Amoxapine (Bagadia et al., 1979[16]) and Loxapine. Lithium Carbonate (Bagadia et al., 1983[13]) was introduced in 1975. This marked a turning point in the way Psychosis was treated and followed-up. Those obviously suffering from Manic Depressive Psychosis were put on Lithium. The short-term and long-term evaluation and follow-up of these patients and periodic Serum Lithium estimations added a special dimension to their treatment in Psychiatry. Bipolar Disorder subsequently came into focus all over the world, and later, anti-epileptic drugs joined the group of mood stabilizers.
Combination drugs
Trifluoperazine, a standard effective antipsychotic drug was being used for psychosis and was prescribed with another drug Trihexyphenidyl HCl — an anticholinergic antiparkinsonian drug to effectively eliminate extrapyramidal side effects. A pharmaceutical company, on suggestions of many Senior Psychiatrists, combined these two drugs into one combination product and named it Trinicalm Plus. It was marketed by Trinity Pharma, later named Torrent Pharma. The product Trinicalm Plus became immensely popular, and Torrent later became a giant in the psychopharmaceutical industry. The reasons for the Trinicalm Plus success were good efficacy, safety, minimal side effects and cost effectiveness. This enabled poor patients to use it and get well. This drug combination trend further developed in India.
Depot antipsychotics/long-acting antipsychotics
They were significant important additions and very useful in treating non-compliant patients with poor insight. They were drugs such as Fluphenazine decanoate and Penfluridol. Newer Antidepressants Nitroxazepine, Dothiepin, Amoxapine and Mianserin were introduced in late 1970s. Though effective they were costly and were used more as second-line alternative drugs or in refractory cases. Loxapine, with tricyclic structure but antipsychotic effect, also had the same fate.
The discovery of newer and better effective molecules is every psychiatrist’s dream. I am sure brilliant clinicians and brilliant research workers together will invent new medicines in the years to come.
Post Graduate Teaching
Post Graduate education, in its present form, is more patient focused. Furthermore, the available variety of patient population in large numbers in this country in general, and Mumbai in particular, is a vastly enriching experience, though it can be strenuous sometimes for post graduate students and their teachers as well.
Psychiatric Camps
Personally, I believe Psychiatric Camps are a convincing way of educating people and making a provisional diagnosis and guiding them to treatment centres in General hospitals. I have conducted 3 such camps in Thane district, 2 in Porbandar, Gujarat, and have organised many camps for the Indian Psychiatric Society-West Zone Conferences.
Future
It is a long path ahead. Understanding the person called the patient, by means of a permissive dialogue is the golden path for good clinical practice and for getting good results. The data thus generated are bound to enhance clinical research, as also basic research, to lead to newer findings and newer treatment modalities, as also in reducing the stigma that bothers all psychiatrists the world over.
Together with you all, I will enjoy this long march for many years to come.
Concluding Remarks
This paper traces a personal journey from 1970 to 1984. It starts from joining the Psychiatry Department of KEM Hospital, Mumbai, India to presenting papers at Zonal and National Conferences, making friends with psychiatric colleagues all over the country, teaching under and post-graduates, conducting psychiatric camps, and working in the WHO Collaborating Center. It also lists the many research projects conducted, and papers published from the Department during this time [Figure 1].
Figure 1.
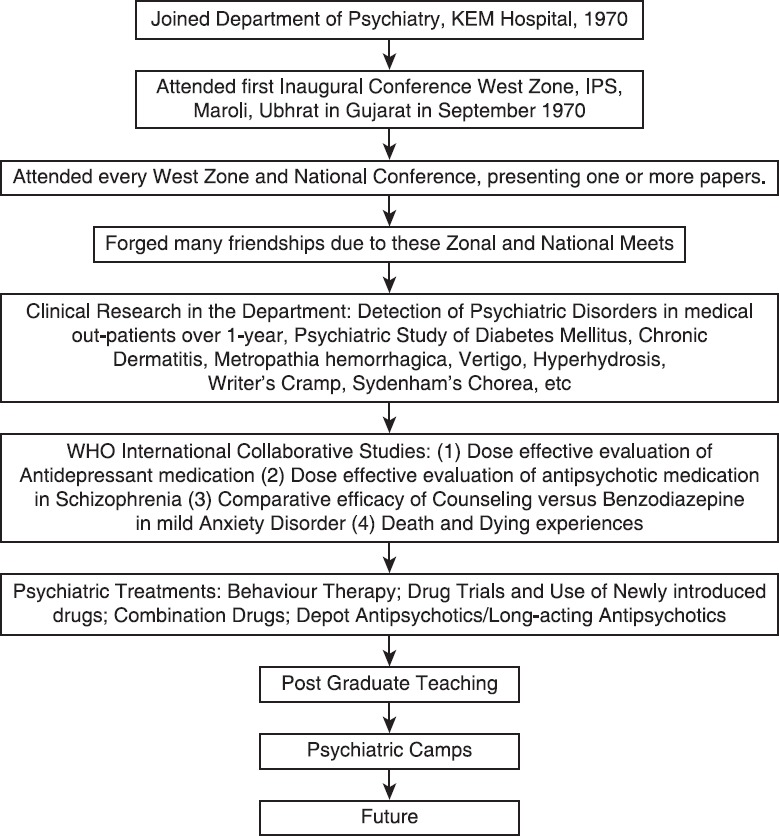
Flowchart of the paper
Take Home Message
The journey, as a psychiatrist of teaching under and post graduates, of doing research and of making friends while attending Conferences, has been an enriching experience.
Questions that this Paper Raises
How important is it to make friends amongst professional colleagues?
Where is present day psychiatry headed?
Do studies of the old hold any significance today?
About the Author

Prakash V. Pradhan MD DPM has been, at various times, Honorary Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Hon. Professor and Acting Chief, Hon. Professor and Unit Chief, G.S. Medical College and K.E.M. Hospital, Parel, Mumbai, India. He has been President, Bombay Psychiatric Society, 1984-1985 and President, Indian Psychiatric Society – West Zone, 1987-1988. He has more than 70 Research papers presented and 52 papers published in National and International Journals on Clinical Research in Psychiatry and Psychosomatic Disorders. He has worked as an examiner for DPM and M.D. degrees of University of Mumbai, Gujarat University, Shivaji University, Kolhapur and College of Physicians and Surgeons, Parel, Mumbai on several occasions. He has conducted the first Psychiatric Camp in Mumbai in 1998 and several others on behalf of Dept. of Psychiatry KEM Hospital, Mumbai in 1999, 2000 and 2001. He has led and participated in Psychiatric Camps held in Porbander Junagadh, in Gujarat, Wada and Shahpur in Thane District.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Declaration
This is my original unpublished paper, not sent for publication elsewhere.
CITATION: Pradhan PV. Looking Back at the Years 1970-1984: A Personal View. Mens Sana Monogr 2015;13:23-30.
Peer reviewer for this paper: Anon
References
- 1.Bagadia VN, Abhyankar RR, Gopalani JH, Jagasia R, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. Maintenance therapy of schizophrenia. Indian J Psychiatry. 1979;21:106–8. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bagadia VN, Ayyar KS, Dhawale KM, Pradhan PV. Treatment of 26 cases of male sexual dysfunction by behaviour modification techniques. Indian J Psychiatry. 1983;25:29–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bagadia VN, Ayyar KS, Pradhan PV, et al. Life stress in dermatology out patients. Arch Indian Psychiatry. 1998;4:47–9. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bagadia VN, Bhat R, Ghadiyali HN, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. A comparative double – Blind trial of pimozide and trifluperazine in maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. Indian J Psychiatry. 1976;18:199–203. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bagadia VN, Bhat R, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. ‘Piportial’ injection (19552-RP) – A depot neuroleptic in schizophenia. Indian J Psychiatry. 1979;21:259–61. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bagadia VN, Dave KP, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. A study of Male patients with sexual problems. Indian J Psychiatry. 1972;14:143–51. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bagadia VN, Dhawle KM, Shah LP, Pradhan PV. Evaluation of disulfiram in the treatment of alcoholism. Indian J Psychiatry. 1982;24:242–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bagadia VN, Ghadiali HN, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. A study of the effects of hospitalization on schizophrenic symptomatology. Neurol India. 1973;21:209–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bagadia VN, Ghadiyali HN, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. Pimozide (R 6238) in schizophrenia. Indian J Psychiatry. 1973;15:319–24. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bagadia VN, Gopalani J, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. Habitual Use of cannabis indica in psychiatric patients. Indian J Psychiatry. 1976;18:141–6. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bagadia VN, Jeste DV, Charegaonkar AS, Pradhan PV, Shah LP. A psycho – Social study of 180 cases of epilepsy. Indian J Psychiatry. 1973;15:391–401. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bagadia VN, Havaldar PP, Gada MT, Pradhan PV, Shah LP, Dhirwani MK. Diabetes mellitus – A psychosomatic study of 147 cases. J Postgrad Med. 1973;21:17–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bagadia VN, Lakdawala PD, Pradhan PV, Mundra VK, Desai NK, Shah LP. Lithium in aggression. Indian J Psychiatry. 1983;25:107–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bagadia VN, Mundra VK, Mistry PP, Pradhan PV. Chronic alcoholism: The responder on electrical aversion therapy. Indian J Psychiatry. 1979;21:64–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bagadia VN, Pradhan PV, Olatwara M, Hirsch SR, Kato M, Vartanian FE, et al. Geneva, Berlin, Germany: Springer Verlag; 1988. In: World Health Organization, editor. Benzodiazepines and Therapeutic Counselling: Report from a WHO Collaborative Study. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bagadia VN, Shah LP, Pradhan PV, Gada MT. A double blind controlled study of amoxapine and imipramine in cases of depression. Curr Ther Res. 1979;26:417–29. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gada MT, Agrawal BR, Pradhan PV, Shah LP, Bagadia VN. Report from a World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborative Centre for Psychopharmacology in India. Survey of antipsychotic drugs use. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1983;19:778–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gada MT, Pradhan PV, Shah LP, Bagadia VN. Antidepressant drugs. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1984;20:180–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pradhan VP, Agarwal BR. Hyperhidrosis – Psychiatric study and behaviour therapy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1984;50:134–6. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pradhan PV, Ayyar KS, Munjal PD, Gopalani JH, Mundra AV, Doshi J, et al. Obsessive compulsive neuroses: Treatment of 28 cases by behaviour therapy. Indian J Psychiatry. 1984;26:71–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pradhan PV, Ayyar KS, Bagadia VN. Homosexuality: Treatment by behaviour modification. Indian J Psychiatry. 1982;24:80–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pradhan PV, Ayyar KS, Bagadia VN. Male homosexuality: A psychiatric study of thirteen cases. Indian J Psychiatry. 1982;24:182–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Singh AR, Bagadia VN, Pradhan PV, Acharya VN. Death, dying and near death experience – Preliminary report on surveying the need and developing the method. Indian J Psychiatry. 1988;30:299–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]

